solo para uso en investigación
PLX-4720 Inhibidor de B-Raf
Cat. No.S1152
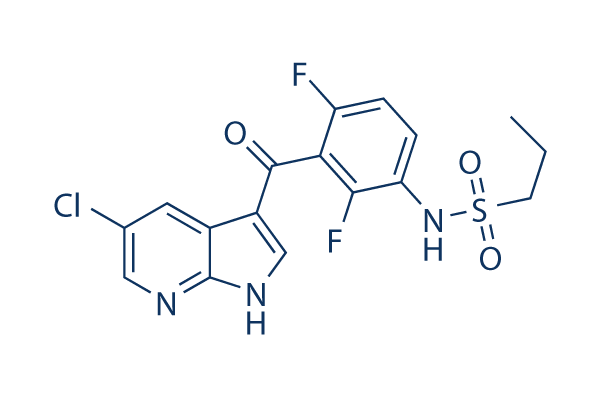
Estructura química
Peso molecular: 413.83
Control de calidad
Productos que se suelen utilizar junto con PLX-4720
| Dianas relacionadas | ERK p38 MAPK JNK MEK Ras KRas S6 Kinase MAP4K TAK1 Mixed Lineage Kinase |
|---|---|
| Otros Raf Inhibidores | LY3009120 Exarafenib (KIN-2787) GDC-0879 Avutometinib (Ro5126766, CH5126766) AZ 628 SB590885 TAK-632 GW5074 RAF265 (CHIR-265) PLX8394 (Plixorafenib, FORE8394) |
Cultivo celular, tratamiento y concentración de trabajo
| Líneas celulares | Tipo de ensayo | Concentración | Tiempo de incubación | Formulación | Descripción de la actividad | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DU-4475 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.07457 μM | SANGER | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.14166 μM | SANGER | |||
| C32 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.15131 μM | SANGER | |||
| M14 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.21757 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP50-MEL-B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.29784 μM | SANGER | |||
| A101D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.32589 μM | SANGER | |||
| G-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.34637 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-144 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.36329 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.38477 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-829 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.38968 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-HO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.41179 μM | SANGER | |||
| SH-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.41422 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.51568 μM | SANGER | |||
| A375 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.67359 μM | SANGER | |||
| MMAC-SF | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.68614 μM | SANGER | |||
| BHT-101 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.70702 μM | SANGER | |||
| K5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.76148 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.79644 μM | SANGER | |||
| RVH-421 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.86796 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2218 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.87844 μM | SANGER | |||
| WM-115 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.88692 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.04569 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-679 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.10464 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ7-mel | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.14963 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-30 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.33386 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H209 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.6086 μM | SANGER | |||
| HTC-C3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.66294 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.04978 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.11969 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.30787 μM | SANGER | |||
| PA-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.72673 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO-3N1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.87946 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H358 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.92232 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.40176 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.55266 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP66-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.15927 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.49179 μM | SANGER | |||
| DBTRG-05MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.53325 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2058 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.72164 μM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.73908 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8305C | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.1873 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-7951 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.80283 μM | SANGER | |||
| CHL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.97603 μM | SANGER | |||
| TI-73 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.00902 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1080 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.10946 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.14924 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8-MG-BA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.18129 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.21373 μM | SANGER | |||
| H4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.22493 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-72 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.45423 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.81931 μM | SANGER | |||
| BCPAP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.21764 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.36907 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-741 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.01679 μM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.07068 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.41516 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCT | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.75314 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.05178 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.56999 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.6048 μM | SANGER | |||
| VA-ES-BJ | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.0149 μM | SANGER | |||
| A431 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.4212 μM | SANGER | |||
| LXF-289 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.458 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.8274 μM | SANGER | |||
| NOS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.8472 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.2404 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-HEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.3527 μM | SANGER | |||
| A3-KAW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.7178 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.2655 μM | SANGER | |||
| TYK-nu | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.3932 μM | SANGER | |||
| NMC-G1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.6062 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.7169 μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.8833 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-566MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9576 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-140 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.0753 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.3359 μM | SANGER | |||
| U251 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.8492 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-542MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9222 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9932 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.2684 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4293 μM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4305 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4458 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7616 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7835 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ2-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.0646 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-12T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.4862 μM | SANGER | |||
| KE-37 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.8107 μM | SANGER | |||
| LS-411N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.118 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2228 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.3071 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.4965 μM | SANGER | |||
| HN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.7248 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1648 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.818 μM | SANGER | |||
| IA-LM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.3172 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5708 μM | SANGER | |||
| YKG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5711 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-81-FD | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5858 μM | SANGER | |||
| 23132-87 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.7642 μM | SANGER | |||
| NUGC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.9887 μM | SANGER | |||
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.0478 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1755 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.4764 μM | SANGER | |||
| RH-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.5748 μM | SANGER | |||
| RXF393 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.6756 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-134-A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7056 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7201 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.1915 μM | SANGER | |||
| IGR-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.3796 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-92 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.4987 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MES-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.7381 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-65 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.8624 μM | SANGER | |||
| MS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.1203 μM | SANGER | |||
| LoVo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.244 μM | SANGER | |||
| A704 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.5155 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6059 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-MEL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6751 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.7366 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.7979 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1197 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.0817 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2518-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.6412 μM | SANGER | |||
| J-RT3-T3-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.7595 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.8744 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.0023 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-SL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.2751 μM | SANGER | |||
| HH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.3192 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.938 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-449 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2018 μM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2813 μM | SANGER | |||
| LOXIMVI | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.368 μM | SANGER | |||
| GR-ST | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.6706 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.944 μM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.1604 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.2814 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.713 μM | SANGER | |||
| EGI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.8845 μM | SANGER | |||
| TCCSUP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.9272 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB996-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.5682 μM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-97TM1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.1964 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1304 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.3301 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.5973 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1770 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.1648 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.6504 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.7236 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACHN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8385 μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8544 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8971 μM | SANGER | |||
| KGN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.7292 μM | SANGER | |||
| U031 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.8132 μM | SANGER | |||
| HMV-II | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.0774 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.6455 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1155 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.0015 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1793 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1026 μM | SANGER | |||
| P30-OHK | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1332 μM | SANGER | |||
| AN3-CA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1615 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-257 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.79 μM | SANGER | |||
| MCF7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.8629 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4285 μM | SANGER | |||
| T98G | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4957 μM | SANGER | |||
| HGC-27 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.274 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1092 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.2895 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.3071 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB1047-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.9959 μM | SANGER | |||
| 786-0 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.65 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2157 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.0359 μM | SANGER | |||
| NY | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.1778 μM | SANGER | |||
| EFM-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7533 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7806 μM | SANGER | |||
| UM-UC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.8059 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-29 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.8792 μM | SANGER | |||
| LN-405 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.0827 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H727 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.7726 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-502MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.9676 μM | SANGER | |||
| GMS-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.2974 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-JUSO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.347 μM | SANGER | |||
| insect cells | Function assay | Inhibition of N-terminal His-tagged BRAF V600E mutant (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells co-expressing CDC37 using biotinylated-MEK as substrate by AlphaScreen assay, IC50 = 0.013 μM. | 29461827 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of BRAF V600E mutant in human A375 cells assessed as reduction in ERK phosphorylation by AlphaScreen assay, IC50 = 0.044 μM. | 29461827 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of b-Raf in human A375 cells assessed phosphorylation of ERK, IC50 = 0.046 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A375 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human A375 cells expressing B-Raf V600E mutant and wild type Ras, IC50 = 0.5 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A375 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A375 cells harboring BRAF V600E mutant after 72 hrs by CellTiter-Glo assay, IC50 = 0.5 μM. | 29461827 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells expressing wild type b-Raf and KRAS mutant, IC50 = 27 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| Haga clic para ver más datos experimentales de líneas celulares | ||||||
Información química, almacenamiento y estabilidad
| Peso molecular | 413.83 | Fórmula | C17H14ClF2N3O3S |
Almacenamiento (Desde la fecha de recepción) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nº CAS | 918505-84-7 | Descargar SDF | Almacenamiento de soluciones madre |
|
|
| Sinónimos | N/A | Smiles | CCCS(=O)(=O)NC1=C(C(=C(C=C1)F)C(=O)C2=CNC3=C2C=C(C=N3)Cl)F | ||
Solubilidad
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(200.56 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calculadora de Molaridad
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculadora de formulación in vivo (Solución clara)
Paso 1: Introduzca la información a continuación (Recomendado: Un animal adicional para tener en cuenta la pérdida durante el experimento)
Paso 2: Introduzca la formulación in vivo (Esto es solo la calculadora, no la formulación. Por favor, contáctenos primero si no hay una formulación in vivo en la sección de Solubilidad.)
Resultados del cálculo:
Concentración de trabajo: mg/ml;
Método para preparar el líquido maestro de DMSO: mg fármaco predissuelto en μL DMSO ( Concentración del líquido maestro mg/mL, Por favor, contáctenos primero si la concentración excede la solubilidad del DMSO del lote del fármaco. )
Método para preparar la formulación in vivo: Tomar μL DMSO líquido maestro, luego añadirμL PEG300, mezclar y clarificar, luego añadirμL Tween 80, mezclar y clarificar, luego añadir μL ddH2O, mezclar y clarificar.
Método para preparar la formulación in vivo: Tomar μL DMSO líquido maestro, luego añadir μL Aceite de maíz, mezclar y clarificar.
Nota: 1. Por favor, asegúrese de que el líquido esté claro antes de añadir el siguiente disolvente.
2. Asegúrese de añadir el (los) disolvente(s) en orden. Debe asegurarse de que la solución obtenida, en la adición anterior, sea una solución clara antes de proceder a añadir el siguiente disolvente. Se pueden utilizar métodos físicos como el vórtice, el ultrasonido o el baño de agua caliente para ayudar a la disolución.
Mecanismo de acción
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
C-Raf-1 (Y340D/Y341D)
(Cell-free assay) 6.7 nM
B-Raf (V600E)
(Cell-free assay) 13 nM
BRK
(Cell-free assay) 130 nM
B-Raf
(Cell-free assay) 160 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
PLX-4720 muestra una selectividad >10 veces mayor contra B-Raf de tipo salvaje, y una selectividad >100 veces mayor sobre otras quinasas como Frk, Src, Fak, FGFR y Aurora A con una IC50 de 1,3-3,4 μM. Este compuesto inhibe significativamente la fosforilación de ERK en líneas celulares que expresan B-RafV600E con una IC50 de 14-46 nM, pero no en las células con B-Raf de tipo salvaje. Inhibe significativamente el crecimiento de líneas celulares tumorales que expresan el oncogén B-RafV600E, como COLO205, A375, WM2664 y COLO829 con una GI50 de 0,31 μM, 0,50 μM, 1,5 μM y 1,7 μM, respectivamente. Además, este tratamiento químico a 1 μM induce la detención del ciclo celular y la apoptosis exclusivamente en las células 1205Lu B-RafV600E-positivas, pero no en las células C8161 con B-Raf de tipo salvaje. Este tratamiento con el compuesto (10 μM) induce significativamente una expresión de BIM >14 veces mayor en las células PTEN+, en comparación con las líneas celulares PTEN- (4 veces), lo que explica la resistencia de las células PTEN- a esta apoptosis inducida por químicos.
|
| Ensayo de quinasa |
Actividades de la quinasa Raf in vitro
|
|
Las actividades de la quinasa Raf de tipo salvaje y de los mutantes in vitro se determinan midiendo la fosforilación de la proteína MEK biotinilada utilizando la tecnología AlphaScreen de Perkin-Elmer. Para cada enzima (0,1 ng), se realizan reacciones de 20 μL en 20 mM Hepes (pH 7,0), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0,01 % Tween-20, 100 nM de proteína biotin-MEK, diversas concentraciones de ATP y concentraciones crecientes de PLX-4720 a temperatura ambiente. Las reacciones se detienen a los 2, 5, 8, 10, 20 y 30 minutos con 5 μL de una solución que contiene 20 mM Hepes (pH 7,0), 200 mM NaCl, 80 mM EDTA y 0,3 % BSA. La solución de detención también incluye el anticuerpo phospho-MEK, microesferas donadoras recubiertas de estreptavidina y microesferas aceptoras de proteína A del kit de detección de proteína A AlphaScreen. El anticuerpo y las microesferas se preincuban en la solución de detención en la oscuridad a temperatura ambiente durante 30 minutos. La dilución final del anticuerpo es 1/2.000, y la concentración final de cada microesfera es 10 μg/mL. Las placas de ensayo se incuban a temperatura ambiente durante una hora y luego se leen en un lector AlphaQuest de PerkinElmer.
|
|
| In vivo |
La administración oral de PLX-4720 a 20 mg/kg/día induce retrasos y regresiones significativos del crecimiento tumoral en xenoinjertos tumorales COLO205 dependientes de B-RafV600E, sin efectos adversos obvios en ratones, incluso a una dosis de 1 g/kg. Este compuesto a 100 mg/kg dos veces al día elimina casi por completo los xenoinjertos 1205Lu que expresan B-RafV600E, mientras que no tiene actividad contra los xenoinjertos C8161 que expresan B-Raf de tipo salvaje. Los efectos antitumorales de este compuesto se correlacionan con el bloqueo de la vía MAPK en aquellas células que albergan la mutación V600E. Este tratamiento químico a 30 mg/kg/día inhibe significativamente el crecimiento tumoral de los xenoinjertos 8505c en >90 %, y disminuye drásticamente las metástasis pulmonares distantes.
|
Referencias |
|
Aplicaciones
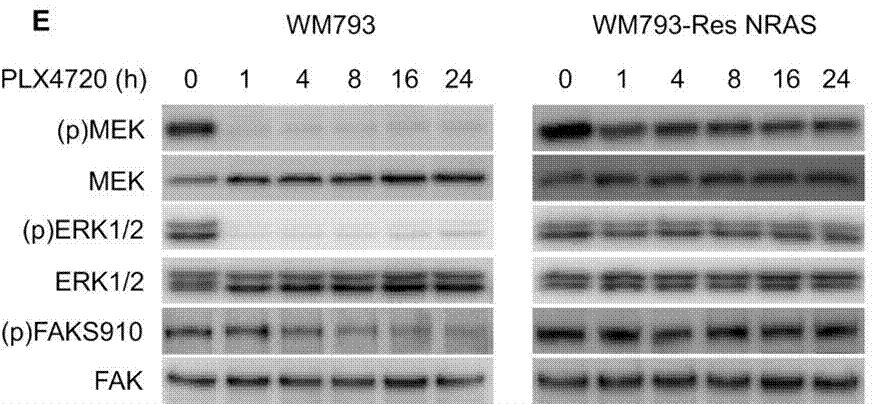
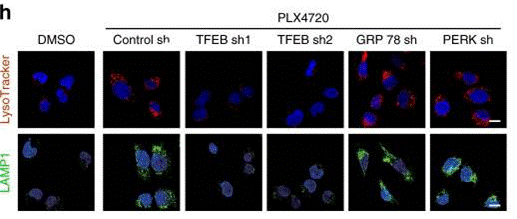
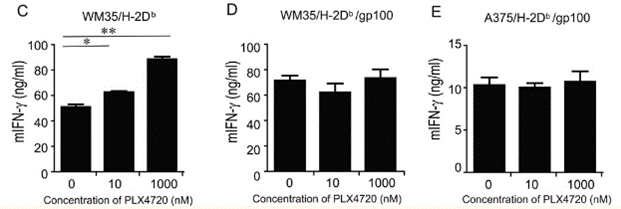
| Métodos | Biomarcadores | Imágenes | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-MEK / MEK / p-ERK / ERK / p-FAK(S910) p-EGFR 1173 / EGFR / p-Akt / Akt p27 / Cyclin D1 / pRb pAkt(Ser473) / pAkt(Thr308) |
|
23076151 |
| Immunofluorescence | LAMP1 ZKSCAN3 / TFEB |
|
30979895 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |

|
27848137 |
| ELISA | mIFN-γ |
|
23204132 |
Soporte técnico
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si tiene alguna otra consulta, por favor deje un mensaje.
Preguntas frecuentes
Pregunta 1:
What would you recommend to make working solution for intraperitoneal injection into mice?
Respuesta:
Due to its very limited solubility in aqueous solution, this compound can be administered as a not fully dissolved suspension via oral gavage. For this reason, we recommend oral gavage for its administration.
