Datos técnicos
| Fórmula | C17H14ClF2N3O3S |
||||||
| Peso molecular | 413.83 | Número CAS | 918505-84-7 | ||||
| Solubilidad (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 82 mg/mL (198.14 mM) | ||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Agregue los solventes al producto individualmente y en orden.) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml significa ligeramente soluble o insoluble. * Tenga en cuenta que Selleck prueba la solubilidad de todos los compuestos internamente, y la solubilidad real puede diferir ligeramente de los valores publicados. Esto es normal y se debe a ligeras variaciones entre lotes. * Envío a temperatura ambiente (Las pruebas de estabilidad demuestran que este producto se puede enviar sin medidas de refrigeración.) |
|||||||
Preparación de soluciones madre
Actividad biológica
| Descripción | PLX4720 es un inhibidor potente y selectivo de B-RafV600E con una IC50 de 13 nM en un ensayo sin células, igualmente potente que c-Raf-1 (mutaciones Y340D y Y341D), con una selectividad 10 veces mayor para B-RafV600E que para B-Raf de tipo salvaje. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objetivos |
|
||||||||
| In vitro | PLX-4720 muestra una selectividad >10 veces mayor contra B-Raf de tipo salvaje, y una selectividad >100 veces mayor sobre otras quinasas como Frk, Src, Fak, FGFR y Aurora A con una IC50 de 1,3-3,4 μM. Este compuesto inhibe significativamente la fosforilación de ERK en líneas celulares que expresan B-RafV600E con una IC50 de 14-46 nM, pero no en las células con B-Raf de tipo salvaje. Inhibe significativamente el crecimiento de líneas celulares tumorales que expresan el oncogén B-RafV600E, como COLO205, A375, WM2664 y COLO829 con una GI50 de 0,31 μM, 0,50 μM, 1,5 μM y 1,7 μM, respectivamente. Además, este tratamiento químico a 1 μM induce la detención del ciclo celular y la apoptosis exclusivamente en las células 1205Lu B-RafV600E-positivas, pero no en las células C8161 con B-Raf de tipo salvaje. Este tratamiento con el compuesto (10 μM) induce significativamente una expresión de BIM >14 veces mayor en las células PTEN+, en comparación con las líneas celulares PTEN- (4 veces), lo que explica la resistencia de las células PTEN- a esta apoptosis inducida por químicos. | ||||||||
| In vivo | La administración oral de PLX-4720 a 20 mg/kg/día induce retrasos y regresiones significativos del crecimiento tumoral en xenoinjertos tumorales COLO205 dependientes de B-RafV600E, sin efectos adversos obvios en ratones, incluso a una dosis de 1 g/kg. Este compuesto a 100 mg/kg dos veces al día elimina casi por completo los xenoinjertos 1205Lu que expresan B-RafV600E, mientras que no tiene actividad contra los xenoinjertos C8161 que expresan B-Raf de tipo salvaje. Los efectos antitumorales de este compuesto se correlacionan con el bloqueo de la vía MAPK en aquellas células que albergan la mutación V600E. Este tratamiento químico a 30 mg/kg/día inhibe significativamente el crecimiento tumoral de los xenoinjertos 8505c en >90 %, y disminuye drásticamente las metástasis pulmonares distantes. |
Protocolo (de referencia)
| Ensayo de quinasa:[1] |
|
|---|---|
| Ensayo celular:[1] |
|
| Estudio en animales:[1] |
|
Referencias
|
Validación de productos por parte del cliente
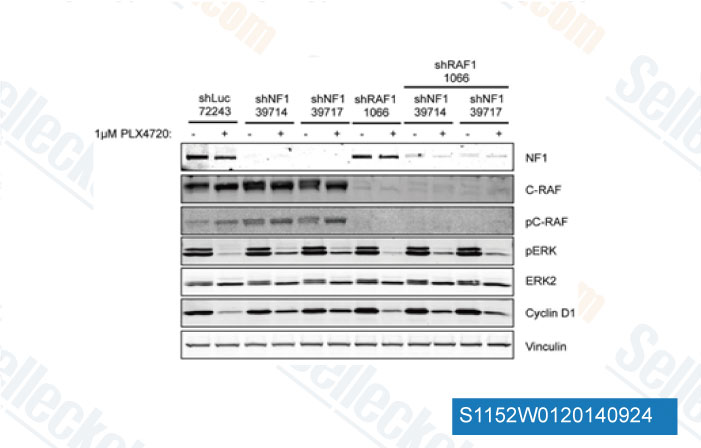
-
Datos de [ Cancer Discov , 2013 , 3, 350-62 ]
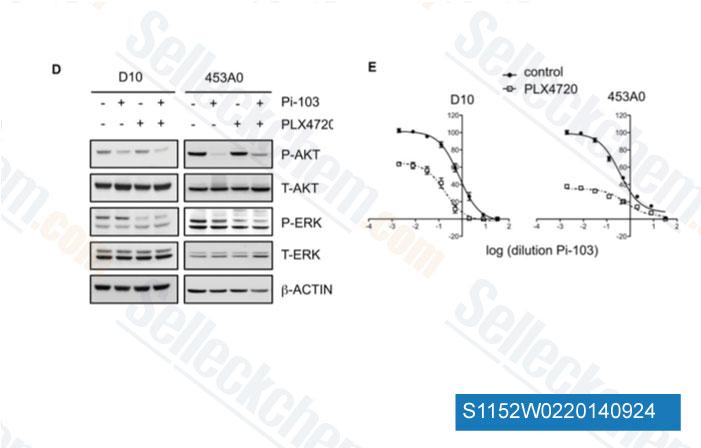
-
Datos de [ Genes Dev , 2012 , 26, 1055-69 ]
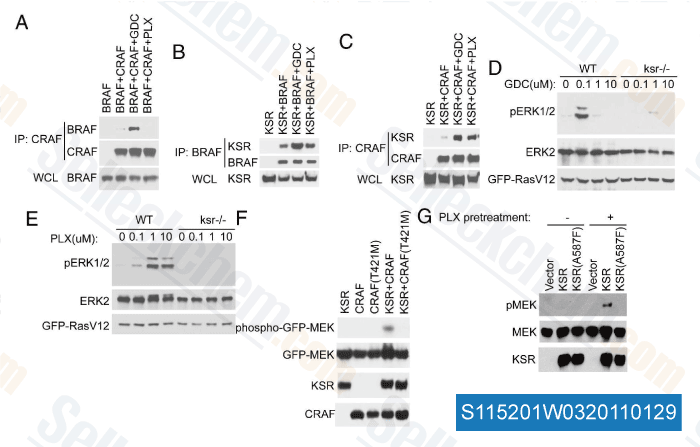
-
Datos de [ Proc Natl Acad Sci USA , 2011 , 108, 6067-6072 ]
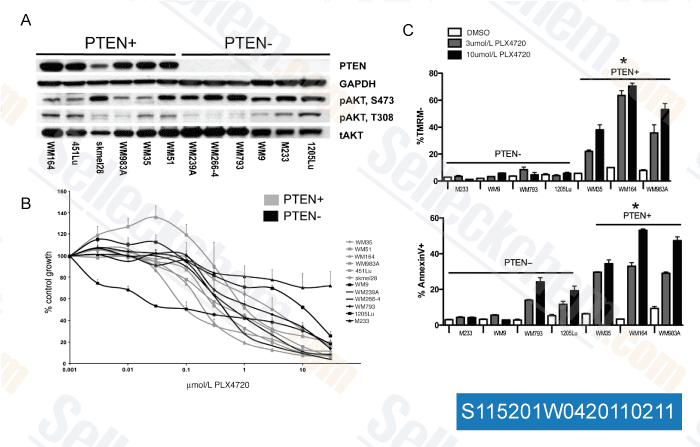
-
Datos de [ Cancer Res , 2011 , 71, 2750-2760 ]
Sellecks PLX-4720 Ha sido citado por 206 Publicaciones
| Elevated NR2F1 underlies the persistence of invasive disease after treatment of BRAF-mutant melanoma [ J Clin Invest, 2025, 135(18)e178446] | PubMed: 40955663 |
| Elevated Transglutaminase-2 in SOX10-Deficient Melanoma Promotes Tumor Onset and Decreases Intratumoral CD4+ T Cells [ Cancer Res, 2025, 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-3267] | PubMed: 40742313 |
| PTRF Confers Melanoma-Acquired Drug Resistance Through the Upregulation of EGFR [ Cell Prolif, 2025, e70086.] | PubMed: 40745979 |
| A functional comparison of two transplantable syngeneic mouse models of melanoma: B16F0 and YUMM1.7 [ Biol Open, 2025, 14(9)bio062175] | PubMed: 40878826 |
| Noncanonical role of Golgi-associated macrophage TAZ in chronic inflammation and tumorigenesis [ Sci Adv, 2025, 11(4):eadq2395] | PubMed: 39841821 |
| The ribotoxic stress response drives UV-mediated cell death [ Cell, 2024, 187(14):3652-3670.e40] | PubMed: 38843833 |
| Tracking the EMT-like phenotype switching during targeted therapy in melanoma by analyzing extracellular vesicle phenotypes [ Biosens Bioelectron, 2024, 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115819] | PubMed: 37952322 |
| Mcl-1 mediates intrinsic resistance to RAF inhibitors in mutant BRAF papillary thyroid carcinoma [ Cell Death Discov, 2024, 10(1):175] | PubMed: 38622136 |
| The ERK5 pathway in BRAFV600E melanoma cells plays a role in development of acquired resistance to dabrafenib but not vemurafenib [ FEBS Lett, 2024, 10.1002/1873-3468.14960] | PubMed: 38977937 |
| Executioner caspases restrict mitochondrial RNA-driven Type I IFN induction during chemotherapy-induced apoptosis [ Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1):1399] | PubMed: 36918588 |
POLÍTICA DE DEVOLUCIÓN
La Política de Devolución Incondicional de Selleck Chemical garantiza una experiencia de compra en línea fluida para nuestros clientes. Si no está satisfecho con su compra de alguna manera, puede devolver cualquier artículo(s) dentro de los 7 días posteriores a su recepción. En caso de problemas de calidad del producto, ya sean problemas relacionados con el protocolo o con el producto, puede devolver cualquier artículo(s) dentro de los 365 días a partir de la fecha de compra original. Siga las instrucciones a continuación al devolver productos.
ENVÍO Y ALMACENAMIENTO
Los productos Selleck se transportan a temperatura ambiente. Si recibe el producto a temperatura ambiente, tenga la seguridad de que el Departamento de Inspección de Calidad de Selleck ha realizado experimentos para verificar que la colocación a temperatura normal durante un mes no afectará la actividad biológica de los productos en polvo. Después de la recogida, guarde el producto de acuerdo con los requisitos descritos en la hoja de datos. La mayoría de los productos Selleck son estables en las condiciones recomendadas.
NO PARA USO HUMANO, DIAGNÓSTICO VETERINARIO O TERAPÉUTICO.
