solo para uso en investigación
Veliparib (ABT-888) PARP inhibidor
Cat. No.S1004
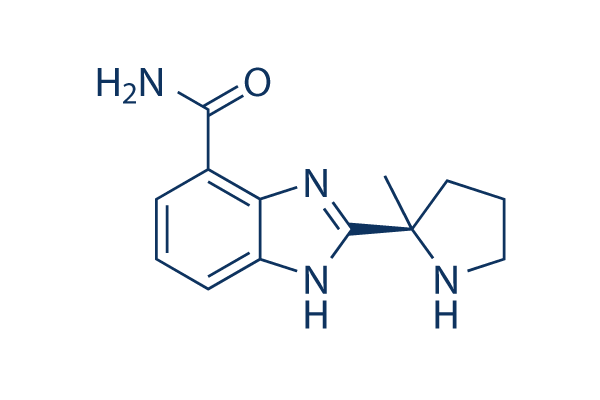
Estructura química
Peso molecular: 244.29
Control de calidad
| Dianas relacionadas | HDAC ATM/ATR DNA-PK WRN DNA/RNA Synthesis Topoisomerase PPAR Sirtuin Casein Kinase eIF |
|---|---|
| Otros PARP Inhibidores | XAV-939 AZD5305 (Saruparib) PJ34 HCl AG-14361 Iniparib (BSI-201) G007-LK Pamiparib UPF 1069 A-966492 Stenoparib (E7449) |
Cultivo celular, tratamiento y concentración de trabajo
| Líneas celulares | Tipo de ensayo | Concentración | Tiempo de incubación | Formulación | Descripción de la actividad | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4-Fuk | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.5691 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.9207 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.2538 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.4818 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1187 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.2771 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB14 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.7031 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.0998 μM | SANGER | |||
| IGROV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.3304 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-54 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.966 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.7018 μM | SANGER | |||
| H4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.567 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.7345 μM | SANGER | |||
| MV-4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.8499 μM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.6001 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.5868 μM | SANGER | |||
| MFE-280 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.3889 μM | SANGER | |||
| KU812 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.3642 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-684 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.3599 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.7457 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.4241 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.4901 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.4798 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3814 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3814 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-139 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3748 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.0235 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB771 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.8373 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.4663 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.434 μM | SANGER | |||
| HAL-01 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.8862 μM | SANGER | |||
| KASUMI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.89266 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.43603 μM | SANGER | |||
| C41 | Kinase Assay | 30 min | Inhibition of PARP1 with EC50 of 0.002 μM | 19888760 | ||
| Jurkat | Kinase Assay | 96 h | DMSO | Inhibition of PARP1 assessed as reduction of cell viability with EC50 of 3 μM | 23850199 | |
| Capan1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | DMSO | Antiproliferative activity against BRCA2 gene mutated human Capan1 cells with IC50 of 39.7 μM | 24398383 | |
| ML-1 | Apoptotic Assay | 2.5 μM | 24 h | DMSO | Synergistically enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in ML-1 cells | 24895135 |
| HCT-116 | Kinase Assay | 0.5 μM | 24 h | PARP activity decreases | 23054213 | |
| UM-SCC1 | Cytotoxic Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | Reduces the cell viability | 21912620 | |
| FaDu | Cytotoxic Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | Reduces the cell viability | 21912620 | |
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| VC8 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | Cytotoxicity against Chinese hamster VC8 cells harboring BRCA2 deficient after 3 days by CCK8 assay, CC50 = 2.344 μM. | 29335205 | ||
| LoVo | Cytotoxicity assay | 0.4 uM | 5 days | Potentiation of -induced cytotoxicity in human LoVo cells assessed as GI50 at 0.4 uM after 5 days by Celltiter-Glo assay, GI50 = 6.203 μM. | 26652717 | |
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| T98G | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.8517 μM | SANGER | |||
| BALL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.9532 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.8414 μM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.3063 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.952 μM | SANGER | |||
| BEN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.9566 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC70 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.7246 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1693 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2898 μM | SANGER | |||
| HLE | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.054 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2029 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.4238 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.8969 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGBC11TKB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.6863 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.746 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-NB-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.1363 μM | SANGER | |||
| A388 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.9091 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7455 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5649 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-150 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.9986 μM | SANGER | |||
| NKM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5119 μM | SANGER | |||
| H9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.2833 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-668 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.6294 μM | SANGER | |||
| GP5d | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.053 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.6717 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.5325 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.2042 μM | SANGER | |||
| OS-RC-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.9589 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.5565 μM | SANGER | |||
| DU-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9053 μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.5389 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.166 μM | SANGER | |||
| HEC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.9196 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.485 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.4752 μM | SANGER | |||
| DT40 | Cytotoxic Assay | 72 h | DMSO | Cytotoxicity against chicken BRCA2-deficient DT40 cells | 24922587 | |
| PC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | Induces a significant inhibition in colony formation | 21571912 | ||
| C41 | Function assay | Inhibition of PARP1 in human C41 cells, EC50 = 0.002 μM. | 19143569 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.0798 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.12841 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.45409 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.75173 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-680 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.21406 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2218 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.79704 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.81924 μM | SANGER | |||
| Mo-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.6389 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-PREB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.7585 μM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.3791 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H510A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.9034 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.7856 μM | SANGER | |||
| Haga clic para ver más datos experimentales de líneas celulares | ||||||
Información química, almacenamiento y estabilidad
| Peso molecular | 244.29 | Fórmula | C13H16N4O |
Almacenamiento (Desde la fecha de recepción) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nº CAS | 912444-00-9 | Descargar SDF | Almacenamiento de soluciones madre |
|
|
| Sinónimos | NSC 737664 | Smiles | CC1(CCCN1)C2=NC3=C(C=CC=C3N2)C(=O)N | ||
Solubilidad
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 49 mg/mL
(200.58 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calculadora de Molaridad
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculadora de formulación in vivo (Solución clara)
Paso 1: Introduzca la información a continuación (Recomendado: Un animal adicional para tener en cuenta la pérdida durante el experimento)
Paso 2: Introduzca la formulación in vivo (Esto es solo la calculadora, no la formulación. Por favor, contáctenos primero si no hay una formulación in vivo en la sección de Solubilidad.)
Resultados del cálculo:
Concentración de trabajo: mg/ml;
Método para preparar el líquido maestro de DMSO: mg fármaco predissuelto en μL DMSO ( Concentración del líquido maestro mg/mL, Por favor, contáctenos primero si la concentración excede la solubilidad del DMSO del lote del fármaco. )
Método para preparar la formulación in vivo: Tomar μL DMSO líquido maestro, luego añadirμL PEG300, mezclar y clarificar, luego añadirμL Tween 80, mezclar y clarificar, luego añadir μL ddH2O, mezclar y clarificar.
Método para preparar la formulación in vivo: Tomar μL DMSO líquido maestro, luego añadir μL Aceite de maíz, mezclar y clarificar.
Nota: 1. Por favor, asegúrese de que el líquido esté claro antes de añadir el siguiente disolvente.
2. Asegúrese de añadir el (los) disolvente(s) en orden. Debe asegurarse de que la solución obtenida, en la adición anterior, sea una solución clara antes de proceder a añadir el siguiente disolvente. Se pueden utilizar métodos físicos como el vórtice, el ultrasonido o el baño de agua caliente para ayudar a la disolución.
Mecanismo de acción
| Características |
Increases the efficacy of common cancer therapies such as radiation and alkylating agents.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PARP2
(Cell-free assay) 2.9 nM(Ki)
PARP1
(Cell-free assay) 5.2 nM(Ki)
|
| In vitro |
Veliparib (ABT-888) es inactivo para SIRT2 (>5 μM). Inhibe la actividad de PARP con una EC50 de 2 nM en células C41. Este compuesto podría disminuir los niveles de PAR tanto en células H460 irradiadas como no irradiadas. También reduce la supervivencia clonogénica e inhibe la reparación del ADN mediante la inhibición de PARP-1 en células H460. Cuando se combina con la radiación, aumenta la apoptosis y la autophagy en células H460. También inhibe la actividad de PARP en células H1299, DU145 y 22RV1 y la inhibición es independiente de la función de p53. A 10 μM, suprime la fracción de supervivencia (SF) en un 43 % en las células clonogénicas H1299. Muestra una radiosensibilidad efectiva en células H1299 óxicas. Además, podría atenuar la SF de las células hipóxicas irradiadas, incluidas H1299, DU145 y 22RV1. |
| Ensayo de quinasa |
Ensayos PARP in vitro
|
|
Los ensayos de PARP para Veliparib (ABT-888) se realizan en un tampón que contiene 50 mM de Tris (pH 8.0), 1 mM de DTT, 1.5 μM de [3H]NAD+ (1.6 μCi/mmol), 200 nM de histona H1 biotinilada, 200 nM de slDNA y 1 nM de enzima PARP-1 o 4 nM de enzima PARP-2. Las reacciones se terminan con 1.5 mM de benzamida, se transfieren a placas Flash de estreptavidina y se cuentan utilizando un contador de centelleo de microplacas TopCount.
|
|
| In vivo |
Veliparib (ABT-888) tiene una biodisponibilidad oral del 56 % al 92 % en ratones, ratas Sprague-Dawley, perros beagle y monos cinomolgos después de la administración oral. Este compuesto (25 mg/kg i.p.) podría mejorar el retraso del crecimiento tumoral en un modelo de xenoinjerto NCI-H460 con buena tolerancia. En combinación con la radiación, disminuye la formación de vasos tumorales. Reduce los niveles intratumorales de PAR en más del 95 % a una dosis de 3 y 12,5 mg/kg en modelos de xenoinjerto A375 y Colo829, y la supresión podría mantenerse con el tiempo. |
Referencias |
|
Aplicaciones
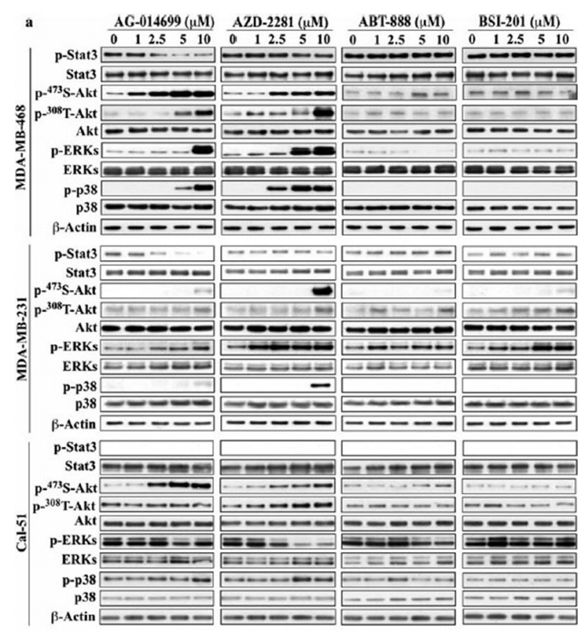
| Métodos | Biomarcadores | Imágenes | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-STAT3 / STAT3 / p-AKT(S473) / p-AKT(T308) / p-ERK / p-p38 |
|
22678161 |
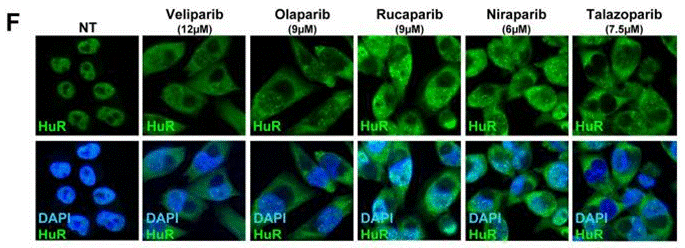
| Immunofluorescence | HuR BRCA1 |
|
28687616 |
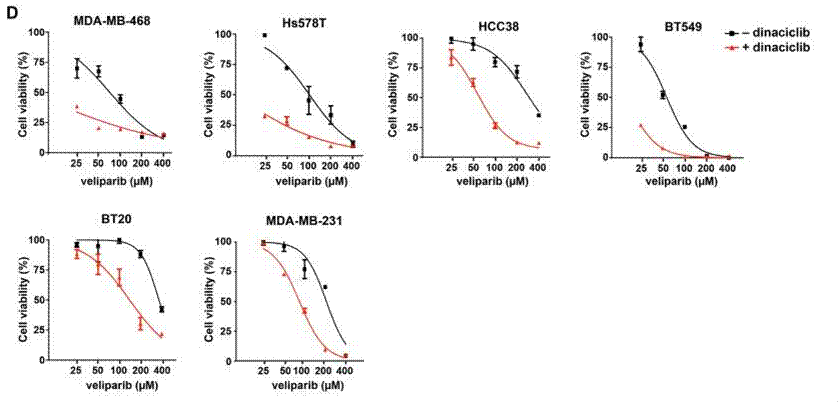
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability (TNBC cell lines) Cell viability (melanoma cells) |
|
27880910 |
Información del ensayo clínico
(datos de https://clinicaltrials.gov, actualizado el 2024-05-22)
| Número NCT | Reclutamiento | Condiciones | Patrocinador/Colaboradores | Fecha de inicio | Fases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03044795 | Withdrawn | Cancer |
University Medical Center Groningen|AbbVie|Dutch Cancer Society |
November 2019 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02723864 | Completed | Neoplasms |
National Cancer Institute (NCI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
August 9 2017 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02483104 | Completed | Ovarian Cancer |
AbbVie |
July 2015 | Phase 1 |
Soporte técnico
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si tiene alguna otra consulta, por favor deje un mensaje.
