solo para uso en investigación
AT9283 JAK inhibidor
Cat. No.S1134
Estructura química
Peso molecular: 381.43
Control de calidad
| Dianas relacionadas | EGFR STAT Pim |
|---|---|
| Otros JAK Inhibidores | BMS-986165 (Deucravacitinib) AZD1480 WP1066 Momelotinib (CYT387) Filgotinib (GLPG0634) Gandotinib (LY2784544) Pacritinib TG101209 Cerdulatinib (PRT062070) hydrochloride NVP-BSK805 2HCl |
Cultivo celular, tratamiento y concentración de trabajo
| Líneas celulares | Tipo de ensayo | Concentración | Tiempo de incubación | Formulación | Descripción de la actividad | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 10 to 14 days | Cytotoxicity against human HCT116 cells assessed as number of colonies after 10 to 14 days by colony forming assay, IC50=0.012μM | 19143567 | ||
| HCT116 | Function assay | 10 mg/kg | Cmax in BALB/c mouse bearing human HCT116 cells at 10 mg/kg, po, Cmax=0.45μM | 19143567 | ||
| HCT116 | Function assay | 5 mg/kg | Cmax in BALB/c mouse bearing human HCT116 cells at 5 mg/kg, iv, Cmax=4.9μM | 19143567 | ||
| HCT116 | Function assay | 20 mg/kg | Cmax in BALB/c mouse bearing human HCT116 cells at 20 mg/kg, ip, Cmax=8.4μM | 19143567 | ||
| HT-29 | Antitumor assay | 72 hrs | Antitumor activity against human HT-29 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.383μM | 23664099 | ||
| A549 | Antitumor assay | 72 hrs | Antitumor activity against human A549 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.512μM | 23664099 | ||
| LoVo | Antitumor assay | 72 hrs | Antitumor activity against human LoVo cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.553μM | 23664099 | ||
| K562 | Antitumor assay | 72 hrs | Antitumor activity against human K562 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=1.6μM | 23664099 | ||
| U937 | Antitumor assay | 72 hrs | Antitumor activity against human U937 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=6.7μM | 23664099 | ||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of His6-tagged MELK catalytic domain (1 to 340 residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Bcl-GL as substrate measured after 30 mins in presence of [gamma32P]ATP by liquid scintillation counting method, IC50=0.685μM | 28351607 | ||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Binding affinity to N-terminal TEV-cleavable hexa-histidine tagged human JAK2 JH1 domain (840 to 1132 residues) expressed in baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells by ITC assay, Kd=0.011μM | 28626521 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Binding affinity to C-terminal thrombin-cleavable hexa-histidine tagged human JAK2 JH2 pseudokinase domain (536 to 812 residues) W659A/W777A/F794H mutant expressed in baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells by ITC assay, Kd=1.323μM | 28626521 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | 10 uM | 60 mins | Displacement of BODIPY-ATP from C-terminal thrombin-cleavable hexa-histidine tagged human JAK2 JH2 pseudokinase domain (536 to 812 residues) W659A/W777A/F794H mutant expressed in baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells at 10 uM after 60 mins by high-throughput flu | 28626521 | |
| HCT116 | Function assay | Inhibition of Aurora B kinase in human HCT116 cells assessed as reduction in polyploid phenotype, IC50=0.03μM | 28918096 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| Haga clic para ver más datos experimentales de líneas celulares | ||||||
Información química, almacenamiento y estabilidad
| Peso molecular | 381.43 | Fórmula | C19H23N7O2 |
Almacenamiento (Desde la fecha de recepción) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nº CAS | 896466-04-9 | Descargar SDF | Almacenamiento de soluciones madre |
|
|
| Sinónimos | N/A | Smiles | C1CC1NC(=O)NC2=C(NN=C2)C3=NC4=C(N3)C=C(C=C4)CN5CCOCC5 | ||
Solubilidad
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 76 mg/mL
(199.25 mM)
Ethanol : 25 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Calculadora de Molaridad
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculadora de formulación in vivo (Solución clara)
Paso 1: Introduzca la información a continuación (Recomendado: Un animal adicional para tener en cuenta la pérdida durante el experimento)
Paso 2: Introduzca la formulación in vivo (Esto es solo la calculadora, no la formulación. Por favor, contáctenos primero si no hay una formulación in vivo en la sección de Solubilidad.)
Resultados del cálculo:
Concentración de trabajo: mg/ml;
Método para preparar el líquido maestro de DMSO: mg fármaco predissuelto en μL DMSO ( Concentración del líquido maestro mg/mL, Por favor, contáctenos primero si la concentración excede la solubilidad del DMSO del lote del fármaco. )
Método para preparar la formulación in vivo: Tomar μL DMSO líquido maestro, luego añadirμL PEG300, mezclar y clarificar, luego añadirμL Tween 80, mezclar y clarificar, luego añadir μL ddH2O, mezclar y clarificar.
Método para preparar la formulación in vivo: Tomar μL DMSO líquido maestro, luego añadir μL Aceite de maíz, mezclar y clarificar.
Nota: 1. Por favor, asegúrese de que el líquido esté claro antes de añadir el siguiente disolvente.
2. Asegúrese de añadir el (los) disolvente(s) en orden. Debe asegurarse de que la solución obtenida, en la adición anterior, sea una solución clara antes de proceder a añadir el siguiente disolvente. Se pueden utilizar métodos físicos como el vórtice, el ultrasonido o el baño de agua caliente para ayudar a la disolución.
Mecanismo de acción
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
JAK3
(Cell-free assay) 1.1 nM
JAK2
(Cell-free assay) 1.2 nM
Aurora A
(Cell-free assay) ~3.0 nM
Aurora B
(Cell-free assay) ~3.0 nM
Abl1 (T315I)
(Cell-free assay) 4 nM
GSK-3β
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM-10 nM
FGFR2
(Cell-free assay) 1-10 nM
VEGFR3/FLT4
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM-10 nM
Mer
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM-10 nM
RET
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM-10 nM
RSK2
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM-10 nM
RSK3
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM-10 nM
TYK2
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM-10 nM
YES
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM-10 nM
Abl (Q252H)
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
DRAK1
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
FGFR1
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
FGFR1 (V561M)
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
FGFR2 (N549H)
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
FGFR3
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
VEGFR1/FLT1
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
FLT3
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
PDGFRα (D842V)
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
PDK-1
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
PKCμ
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
RSK4
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
Src (T341M)
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
VEGFR2
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM-30 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
AT9283 induce un fenotipo poliploide claro al inhibir la actividad de Aurora B kinase en células HCT116 con una IC50 de 30 nM. Además, este compuesto también produce una potente inhibición en la formación de colonias de HCT116. |
| Ensayo de quinasa |
Ensayos de Aurora A y Aurora B Kinase
|
|
Los ensayos para Aurora A y B se realizan en formato DELFIA. La enzima Aurora A se incuba con AT9283 y 3 μM de sustrato cross-tide (biotina-CGPKGPGRRGRRRTSSFAEG) en 10 mM MOPS, pH 7, 0,1 mg/mL BSA, 0,001% Brij-35, 0,5% glicerol, 0,2 mM EDTA, 10 mM MgCl2, 0,01% β-mercaptoetanol, 15 μM ATP y 2,5% DMSO. La enzima Aurora B se incuba con este compuesto, 3 μM del sustrato anterior en 25 mM Tris, pH 8,5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0,1 mg/mL BSA, 0,025% Tween-20, 1 mM DTT, 15 μM ATP y 2,5% DMSO. Las reacciones se dejan proceder durante 60 minutos y 45-90 minutos para Aurora A y Aurora B, respectivamente, antes de ser detenidas con EDTA. Las mezclas de reacción se transfieren luego a una placa recubierta de neutravidina, y el péptido fosforilado se cuantifica mediante un anticuerpo fosfo-específico y un anticuerpo secundario marcado con europio utilizando fluorescencia resuelta en el tiempo (excitación, 337 nm; emisión, 620 nm). Los valores de IC50 para los compuestos de control son 92 nM (ensayo de Aurora A) y 17 nM (ensayo de Aurora B).
|
|
| In vivo |
En ratones con xenoinjertos de carcinoma de colon humano HCT116, el tratamiento con AT9283 (15 mg/kg y 20 mg/kg) durante 16 días resulta en una inhibición significativa del crecimiento tumoral del 67% y 76%, respectivamente. Además, este compuesto también exhibe una vida media significativamente más larga en tumores (2,5 horas) en comparación con el plasma (0,5 horas) y una biodisponibilidad oral modesta en ratones (Fp.o. = 24%). |
Referencias |
|
Aplicaciones
| Métodos | Biomarcadores | Imágenes | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
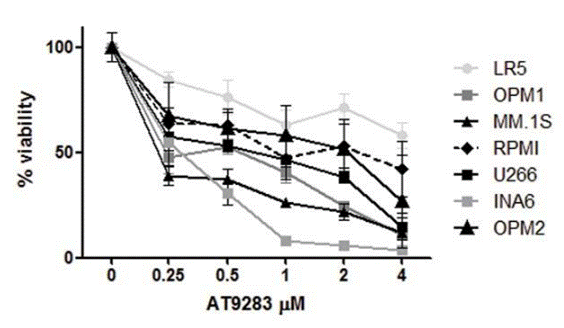
|
21430070 |
Información del ensayo clínico
(datos de https://clinicaltrials.gov, actualizado el 2024-05-22)
| Número NCT | Reclutamiento | Condiciones | Patrocinador/Colaboradores | Fecha de inicio | Fases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01145989 | Completed | Multiple Myeloma |
NCIC Clinical Trials Group|Astex Pharmaceuticals Inc.|Canadian Cancer Trials Group |
February 15 2011 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00443976 | Completed | Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma|Unspecified Adult Solid Tumor Protocol Specific |
NCIC Clinical Trials Group|Astex Pharmaceuticals Inc.|Canadian Cancer Trials Group |
January 30 2007 | Phase 1 |
Soporte técnico
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si tiene alguna otra consulta, por favor deje un mensaje.
