EGFR is a trans-membrane receptor belonging to the erbB/HER-family of RTK. EGFR exists on the cell surface and can be activated by EGF and TGF-alpha. Many important signaling cascades, like MAPK, Akt, and JNK pathways, could be the downstream of EGFR. [show the full text]
EGFR remmers (EGFR Inhibitors)
Overige Protein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitoren
Isoform-selectieve producten
| Cat.nr. | Productnaam | Informatie | Productgebruik Citaten | Productvalidaties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
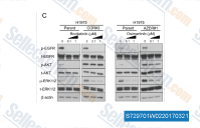
| S7297 | AZD9291 (Osimertinib) | Osimertinib (AZD9291) es un inhibidor de EGFR oral, irreversible y mutante-selectivo con una IC50 de 12,92, 11,44 y 493,8 nM para EGFR con deleción del Exón 19, EGFR L858R/T790M y EGFR WT en células LoVo, respectivamente. Fase 3. |
|
|
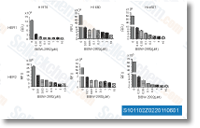
| S1011 | Afatinib (BIBW2992) | Afatinib inhibe EGFR/ErbB irreversiblemente in vitro con IC50 de 0,5, 0,4, 10, 14, 1 nM para EGFRwt, EGFR L858R , EGFR L858R/T790M ErbB2 (HER2) y ErbB4 (HER4), respectivamente. Este compuesto induce la autofagia. |
|
|
| S8724 | Lazertinib (YH25448) | Lazertinib (YH25448,GNS-1480) es un EGFR-TKI potente, altamente selectivo para mutantes e irreversible, con valores de IC50 de 1,7 nM, 2 nM, 5 nM, 20,6 nM y 76 nM para Del19/T790M, L858R/T790M, Del19, L85R y EGFR de tipo salvaje, respectivamente, mostrando valores de IC50 mucho más altos contra ErbB2 y ErbB4. |
|
|
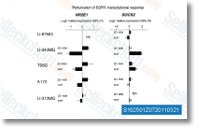
| S1025 | Gefitinib (ZD1839) | Gefitinib es un inhibidor de EGFR para Tyr1173, Tyr992, Tyr1173 y Tyr992 en las células NR6wtEGFR y NR6W con IC50 de 37 nM, 37 nM, 26 nM y 57 nM, respectivamente. Este compuesto promueve la autophagy y la apoptosis de las células de cáncer de pulmón mediante el bloqueo de la vía PI3K/AKT/mTOR. |
|
|
| E4884 | Icotinib Hydrochloride | Icotinib Hydrochloride (BPI-2009H) es un inhibidor de la tirosina quinasa del receptor del factor de crecimiento epidérmico (EGFR-TKI) altamente potente y selectivo con una IC50 de 5 nM, utilizado en el tratamiento del cáncer de pulmón no microcítico (CPNM). | ||
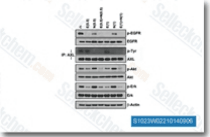
| S7786 | Erlotinib (CP-358774) | Erlotinib es un inhibidor de EGFR con una IC50 de 2 nM, >1000 veces más sensible para EGFR que la c-Src o v-Abl humana. Erlotinib induce Autophagy. |
|
|
| E5906New | Sunvozertinib | Sunvozertinib (DZD9008) es un inhibidor oral, potente y selectivo de las ErbBs (EGFR o Her2), particularmente de las formas mutantes de las ErbBs. También inhibe la EGFR exon 20 NPH insertion, la EGFR exon 20 ASV insertion, las mutaciones EGFR L858R y T790M mutations, la Her2 exon 20 YVMA y la EGFR WT A431, con valores de CI50 de 20,4 nM, 20,4 nM, 1,1 nM, 7,5 nM y 80,4 nM, respectivamente. |
|
|
| S1023 | Erlotinib (CP-358774) Hydrochloride | Erlotinib HCl es un inhibidor de EGFR con un IC50 de 2 nM en ensayos sin células, >1000 veces más sensible para EGFR que c-Src humana o v-Abl. |
|

|
| S2150 | Neratinib (HKI-272) | Neratinib es un inhibidor altamente selectivo de HER2 y EGFR con IC50 de 59 nM y 92 nM en ensayos sin células; inhibe débilmente KDR y Src, sin inhibición significativa de Akt, CDK1/2/4, IKK-2, MK-2, PDK1, c-Raf y c-Met. Fase 3. |
|
|
| S8362 | Tucatinib (Irbinitinib, ONT-380, Arry-380) | Tucatinib (Irbinitinib, ONT-380, ARRY-380) es un inhibidor oral, potente, selectivo, reversible y competitivo de ATP de molécula pequeña de ErbB-2 (también llamado HER2) con CI50 de 8 nM y 7 nM para ErbB-2 y p95 HER2, respectivamente en ensayos basados en células, mostrando una selectividad ~500 veces mayor para HER2 frente a EGFR. Tiene actividad antineoplásica potencial. |
|
|
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) was initially discovered in 1962 following the identification of the ligand EGF. Following this, the role of EGFR in protein phosphorylation and tumorigenesis has been established, and the EGF-EGFR signaling axis has consequently been the focus of research in oncology and developmental biology. Situated in the plasma membrane, EGFR has been an attractive target for anticancer therapy as it becomes activated upon ligand binding, recruiting a number of downstream molecules that leads to the activation of major pathways implicated in tumor growth, progression, and survival.[1][2]
EGFR belongs to the ErbB/HER receptor tyrosine kinase family that encompasses HER2 (ErbB2), HER3 (ErbB3), and HER4 (ErbB4).ii Each constituent of the EGFR family shares a basic domain structure including an N-terminal extracellular domain (subdivided in to domains I through IV), a transmembrane domain, an intracellular kinase domain, and a cytoplasmic C-terminal tail containing several phosphorylation sites that serve as signal transduction modules. The binding of one of several ligands to the extracellular ligand-binding domain induces receptor homo-dimerization or hetero-dimerization and results in kinase activation. Among the EGFR family, it should be noted that ErbB2 is an orphan receptor, characterized by ligand-induced hetero-dimerization with any other family member for activation. Research on ErbB3 initially did not show any intrinsic kinase activity, although recent research findings suggest otherwise.[3]
In the initial activation response of HER family constituents and similar receptor tyrosine kinases are downregulation events, involving ligand-stimulated endocytosis of occupied receptor accompanied by receptor ubiquitination and followed by lysosomal degradation of both ligands and receptors. Another possibility is that receptor tyrosine kinases are recycled from endosomes to the plasma membrane. Interestingly, HER2 and HER3 are internalized and targeted to lysosomes less efficiently than EGFR, and increased expression of HER2 or HER3 can have a dominant-negative effect on EGFR downregulation and degradation. Whether degradation and/or recycling events occur will affect the number of receptors and thus downstream signalling, profoundly changing the biological response.[2]
Ligands of EGFR include EGF, transforming growth factor-α, and heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Once bound to its ligand, EGFR recruits, phosphorylates and activates all of the following downstream signalling cascades: MAPK, PLC-ϒ/PKC, Ras-Raf-Mek, PI3K-Akt-mTOR/PKB and JAK2-STAT3.[1][2] EGFR can also mediate cellular processes through the physical interaction with other proteins in the absence of kinase activity or ligand activation.[1]
Several EGFR-targeting small molecule kinase inhibitors and therapeutic antibodies have been approved by the FDA to treat patients with breast cancer, colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), head and neck-related squamous cell carcinoma and pancreatic cancer. Despite the role that the EGFR signalling pathway plays in several downstream events that lead to tumorigenesis, currently approved EGFR-targeted therapies show only modest effect on most cancer types.[1]
Of the classes of compounds that are in clinical trials and/or are approved for clinical practice use, there are two molecular approaches to target EGFR: (1) monoclonal antibodies, directed against the external ligand-binding site of the receptor (i.e. cetuximab and panitumumab), and (2) small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors, directed against intracellular tyrosine kinase domain (i.e. gefitinib, erlotinib, and lapatinib). In either case, both classes of compounds target EGFR homodimers and heterodimers. Evidence of this includes the ability of erlotinib to target both EGFR and HER3. Interestingly, the impact of monoclonal antibodies targeting EGFR or HER2 is observed to impact VEGFR expression. EGFR affects VEGFR activity through the MAPK and PI3K signalling pathways and at least three different transcription factors, STAT3, Sp1 and hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs).ii A close relative of EGFR is EGFRvIII, found to be localized on the cell-surface where it activates several signalling molecules; overexpression of EGFRvIII has been implicated in malignant gliomas. In tumorigenesis, both EGFR and EGFRvIII are observed to be involved in malignant phenotypes in human cancers.[1]
ErbB proteins are highlighted in oncology research for their ability to drive proliferation, survival, and differentiation. Their overexpression in a variety of human cancers qualifies them as an ideal target for further investigation.[3]
