Solo para uso en investigación
GBE1 Antibody [P1M6]
Nº de cat.: F4945
Aplicación:
Reactividad:
Información de uso
| Dilución |
|---|
|
| Aplicación |
|---|
| WB |
| Reactividad |
|---|
| Human |
| Fuente |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Tampón de almacenamiento |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Almacenamiento (desde la fecha de recepción) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| PM predicho |
|---|
| 76 kDa,80 kDa |
| Control positivo | Human fetal liver tissue; Human skeletal muscle tissue; PC-3 cells |
|---|---|
| Control negativo |
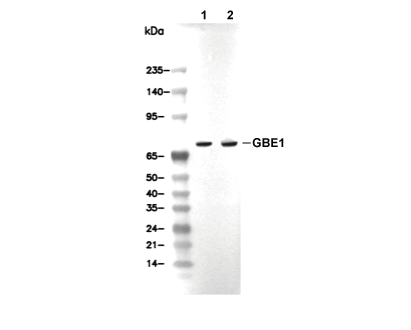
Métodos experimentales
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 120 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
Descripción biológica
| Especificidad |
|---|
| GBE1 Antibody [P1M6] detects endogenous levels of total GBE1 protein. |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| Q04446 |
| Clon |
|---|
| P1M6 |
| Sinónimo |
|---|
| Brancher enzyme; Glycogen-branching enzyme; GBE1 |
| Antecedentes |
|---|
| GBE1 (glycogen branching enzyme 1) encodes a vital glycosyltransferase responsible for introducing α-1,6-glycosidic branch points into linear α-1,4-glucose chains, a process essential for the synthesis of compact, soluble glycogen granules predominantly in liver and muscle, thereby supporting energy homeostasis. It features an N-terminal helical segment, a carbohydrate-binding module 48 (CBM48, residues 76–183), a central (βα)8 catalytic barrel harboring the Asp357-Glu412-Asp481 catalytic triad and Tyr329 substrate-binding cleft, and a C-terminal amylase-like barrel domain; most pathogenic mutations cluster in the catalytic region, disrupting protein folding or glucosyl transfer activity. GBE1 operates downstream of glycogen synthase to generate branched glycogen structures that are rapidly mobilized by phosphorylase during fasting or exercise, crucial for glucose balance. Biallelic GBE1 mutations cause glycogen storage disease type IV (GSD IV, Andersen disease), characterized by absent or reduced enzyme activity, accumulation of insoluble polyglucosan bodies, hepatic failure, myopathy, and infantile lethality in severe forms, whereas partial deficiency, such as the p.Tyr329Ser mutation prevalent in Ashkenazi Jews, leads to adult polyglucosan body disease (APBD), marked by progressive neurodegeneration, spasticity, and neurogenic bladder due to CNS polyglucosan accumulation. |
| Referencias |
|---|
|
Soporte técnico
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si tiene alguna otra consulta, por favor deje un mensaje.