réservé à la recherche
Veliparib (ABT-888) PARP inhibiteur
N° Cat.S1004
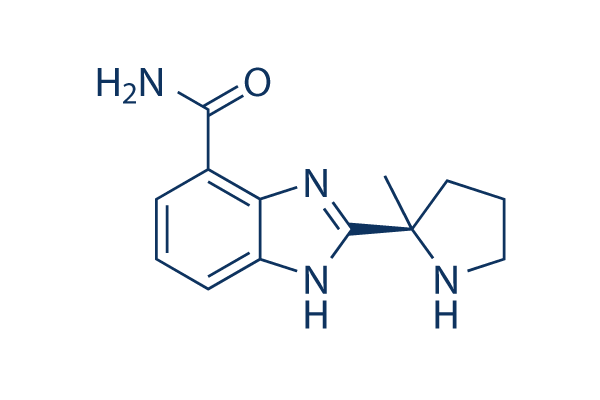
Structure chimique
Poids moléculaire: 244.29
Contrôle qualité
| Cibles apparentées | HDAC ATM/ATR DNA-PK WRN DNA/RNA Synthesis Topoisomerase PPAR Sirtuin Casein Kinase eIF |
|---|---|
| Autre PARP Inhibiteurs | XAV-939 AZD5305 (Saruparib) PJ34 HCl AG-14361 Iniparib (BSI-201) G007-LK Pamiparib UPF 1069 A-966492 Stenoparib (E7449) |
Culture cellulaire, traitement et concentration de travail
| Lignées cellulaires | Type dessai | Concentration | Temps dincubation | Formulation | Description de lactivité | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4-Fuk | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.5691 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.9207 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.2538 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.4818 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1187 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.2771 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB14 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.7031 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.0998 μM | SANGER | |||
| IGROV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.3304 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-54 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.966 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.7018 μM | SANGER | |||
| H4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.567 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.7345 μM | SANGER | |||
| MV-4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.8499 μM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.6001 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.5868 μM | SANGER | |||
| MFE-280 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.3889 μM | SANGER | |||
| KU812 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.3642 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-684 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.3599 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.7457 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.4241 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.4901 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.4798 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3814 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3814 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-139 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3748 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.0235 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB771 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.8373 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.4663 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.434 μM | SANGER | |||
| HAL-01 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.8862 μM | SANGER | |||
| KASUMI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.89266 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.43603 μM | SANGER | |||
| C41 | Kinase Assay | 30 min | Inhibition of PARP1 with EC50 of 0.002 μM | 19888760 | ||
| Jurkat | Kinase Assay | 96 h | DMSO | Inhibition of PARP1 assessed as reduction of cell viability with EC50 of 3 μM | 23850199 | |
| Capan1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | DMSO | Antiproliferative activity against BRCA2 gene mutated human Capan1 cells with IC50 of 39.7 μM | 24398383 | |
| ML-1 | Apoptotic Assay | 2.5 μM | 24 h | DMSO | Synergistically enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in ML-1 cells | 24895135 |
| HCT-116 | Kinase Assay | 0.5 μM | 24 h | PARP activity decreases | 23054213 | |
| UM-SCC1 | Cytotoxic Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | Reduces the cell viability | 21912620 | |
| FaDu | Cytotoxic Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | Reduces the cell viability | 21912620 | |
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| VC8 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | Cytotoxicity against Chinese hamster VC8 cells harboring BRCA2 deficient after 3 days by CCK8 assay, CC50 = 2.344 μM. | 29335205 | ||
| LoVo | Cytotoxicity assay | 0.4 uM | 5 days | Potentiation of -induced cytotoxicity in human LoVo cells assessed as GI50 at 0.4 uM after 5 days by Celltiter-Glo assay, GI50 = 6.203 μM. | 26652717 | |
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| T98G | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.8517 μM | SANGER | |||
| BALL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.9532 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.8414 μM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.3063 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.952 μM | SANGER | |||
| BEN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.9566 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC70 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.7246 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1693 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2898 μM | SANGER | |||
| HLE | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.054 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2029 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.4238 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.8969 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGBC11TKB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.6863 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.746 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-NB-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.1363 μM | SANGER | |||
| A388 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.9091 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7455 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5649 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-150 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.9986 μM | SANGER | |||
| NKM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5119 μM | SANGER | |||
| H9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.2833 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-668 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.6294 μM | SANGER | |||
| GP5d | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.053 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.6717 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.5325 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.2042 μM | SANGER | |||
| OS-RC-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.9589 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.5565 μM | SANGER | |||
| DU-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9053 μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.5389 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.166 μM | SANGER | |||
| HEC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.9196 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.485 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.4752 μM | SANGER | |||
| DT40 | Cytotoxic Assay | 72 h | DMSO | Cytotoxicity against chicken BRCA2-deficient DT40 cells | 24922587 | |
| PC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | Induces a significant inhibition in colony formation | 21571912 | ||
| C41 | Function assay | Inhibition of PARP1 in human C41 cells, EC50 = 0.002 μM. | 19143569 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.0798 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.12841 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.45409 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.75173 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-680 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.21406 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2218 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.79704 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.81924 μM | SANGER | |||
| Mo-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.6389 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-PREB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.7585 μM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.3791 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H510A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.9034 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.7856 μM | SANGER | |||
| Cliquez pour voir plus de données expérimentales sur les lignées cellulaires | ||||||
Informations chimiques, stockage et stabilité
| Poids moléculaire | 244.29 | Formule | C13H16N4O |
Stockage (À partir de la date de réception) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° CAS | 912444-00-9 | Télécharger le SDF | Stockage des solutions mères |
|
|
| Synonymes | NSC 737664 | Smiles | CC1(CCCN1)C2=NC3=C(C=CC=C3N2)C(=O)N | ||
Solubilité
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 49 mg/mL
(200.58 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calculateur de molarité
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculateur de formulation in vivo (Solution claire)
Étape 1 : Entrez les informations ci-dessous (Recommandé : Un animal supplémentaire pour tenir compte des pertes pendant lexpérience)
Étape 2 : Entrez la formulation in vivo (Ceci nest que le calculateur, pas la formulation. Veuillez nous contacter dabord sil ny a pas de formulation in vivo dans la section Solubilité.)
Résultats du calcul :
Concentration de travail : mg/ml;
Méthode de préparation du liquide maître DMSO : mg médicament prédissous dans μL DMSO ( Concentration du liquide maître mg/mL, Veuillez nous contacter dabord si la concentration dépasse la solubilité du DMSO du lot de médicament. )
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, ajouter ensuiteμL PEG300, mélanger et clarifier, ajouter ensuiteμL Tween 80, mélanger et clarifier, ajouter ensuite μL ddH2O, mélanger et clarifier.
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, ajouter ensuite μL Huile de maïs, mélanger et clarifier.
Remarque : 1. Assurez-vous que le liquide est clair avant dajouter le solvant suivant.
2. Assurez-vous dajouter le(s) solvant(s) dans lordre. Vous devez vous assurer que la solution obtenue lors de lajout précédent est une solution claire avant de procéder à lajout du solvant suivant. Des méthodes physiques telles que le vortex, les ultrasons ou le bain-marie peuvent être utilisées pour faciliter la dissolution.
Mécanisme daction
| Fonctionnalités |
Increases the efficacy of common cancer therapies such as radiation and alkylating agents.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PARP2
(Cell-free assay) 2.9 nM(Ki)
PARP1
(Cell-free assay) 5.2 nM(Ki)
|
| In vitro |
Veliparib (ABT-888) est inactif contre SIRT2 (>5 µM). Il inhibe l'activité PARP avec une CE50 de 2 nM dans les cellules C41. Ce composé peut diminuer les niveaux de PAR dans les cellules H460 irradiées et non irradiées. Il réduit également la survie clonogénique et inhibe la réparation de l'ADN par l'inhibition de PARP-1 dans les cellules H460. En combinaison avec la radiation, il augmente l'apoptosis et l'autophagy dans les cellules H460. Il inhibe également l'activité PARP dans les cellules H1299, DU145 et 22RV1 et l'inhibition est indépendante de la fonction p53. À 10 µM, il supprime la fraction de survie (SF) de 43% dans les cellules clonogéniques H1299. Il montre une radiosensibilité efficace dans les cellules H1299 oxiques. De plus, il peut atténuer la SF des cellules hypoxiques irradiées, y compris H1299, DU145 et 22RV1. |
| Kinase Assay |
Tests PARP in vitro
|
|
Les essais PARP pour Veliparib (ABT-888) sont effectués dans un tampon contenant 50 mM Tris (pH 8,0), 1 mM DTT, 1,5 μM [3H]NAD+ (1,6 μCi/mmol), 200 nM d'histone H1 biotinylée, 200 nM d'ADN simple brin, et 1 nM d'enzyme PARP-1 ou 4 nM d'enzyme PARP-2. Les réactions sont terminées avec 1,5 mM de benzamide, transférées sur des plaques Flash à la streptavidine, et comptées à l'aide d'un compteur à scintillation de microplaques TopCount.
|
|
| In vivo |
Veliparib (ABT-888) a une biodisponibilité orale de 56%-92% chez les souris, les rats Sprague-Dawley, les chiens beagle et les singes cynomolgus après administration orale. Ce composé (25 mg/kg i.p.) peut améliorer le retard de croissance tumorale dans un modèle de xénogreffe NCI-H460 avec une bonne tolérance. En combinaison avec la radiothérapie, il diminue la formation de vaisseaux tumoraux. Il réduit les niveaux de PAR intratumoraux de plus de 95% à une dose de 3 et 12,5 mg/kg dans les modèles de xénogreffe A375 et Colo829 et la suppression peut être maintenue dans le temps. |
Références |
|
Applications
| Méthodes | Biomarqueurs | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-STAT3 / STAT3 / p-AKT(S473) / p-AKT(T308) / p-ERK / p-p38 |
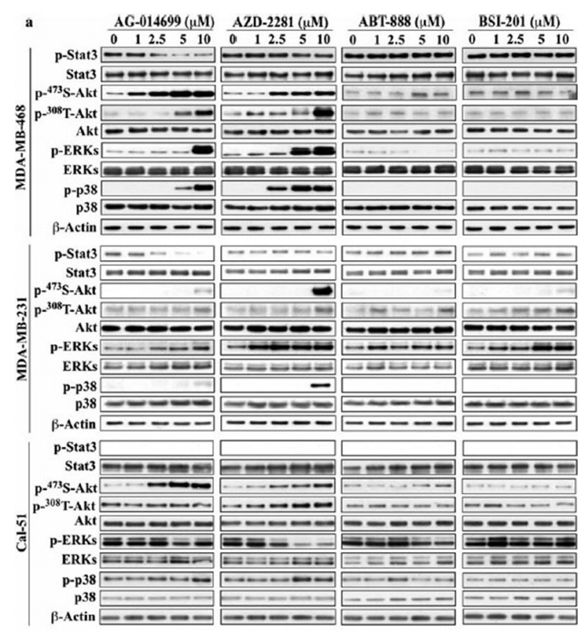
|
22678161 |
| Immunofluorescence | HuR BRCA1 |
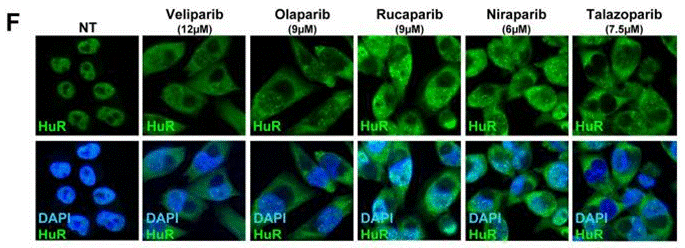
|
28687616 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability (TNBC cell lines) Cell viability (melanoma cells) |
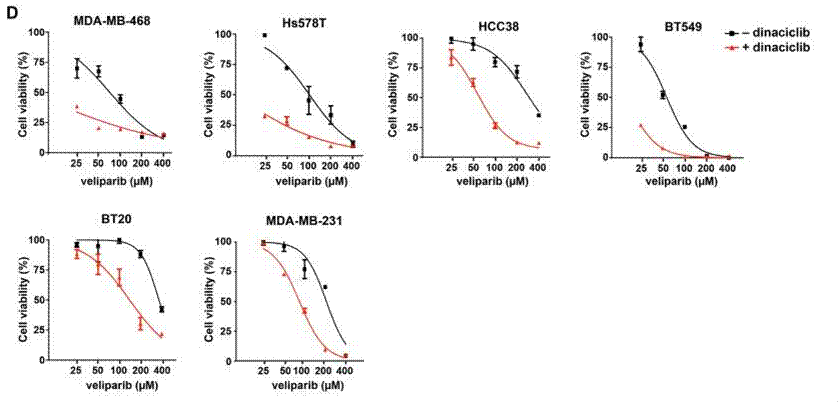
|
27880910 |
Informations sur lessai clinique
(données de https://clinicaltrials.gov, mis à jour le 2024-05-22)
| Numéro NCT | Recrutement | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborateurs | Date de début | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03044795 | Withdrawn | Cancer |
University Medical Center Groningen|AbbVie|Dutch Cancer Society |
November 2019 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02723864 | Completed | Neoplasms |
National Cancer Institute (NCI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
August 9 2017 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02483104 | Completed | Ovarian Cancer |
AbbVie |
July 2015 | Phase 1 |
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.
