Datos técnicos
| Fórmula | C16H15ClN4O2 |
||||||
| Peso molecular | 330.77 | Número CAS | 263707-16-0 | ||||
| Solubilidad (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 66 mg/mL (199.53 mM) | ||||
| Ethanol | 17 mg/mL (51.39 mM) | ||||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Agregue los solventes al producto individualmente y en orden.) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml significa ligeramente soluble o insoluble. * Tenga en cuenta que Selleck prueba la solubilidad de todos los compuestos internamente, y la solubilidad real puede diferir ligeramente de los valores publicados. Esto es normal y se debe a ligeras variaciones entre lotes. * Envío a temperatura ambiente (Las pruebas de estabilidad demuestran que este producto se puede enviar sin medidas de refrigeración.) |
|||||||
Preparación de soluciones madre
Actividad biológica
| Descripción | ESI-09 es un inhibidor específico de la proteína de intercambio directamente activada por cAMP (EPAC) con una IC50 de 3,2 μM y 1,4 μM para EPAC1 y EPAC2, respectivamente, >100 veces más selectivo que la PKA. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objetivos |
|
||||
| In vitro | ESI-09, un nuevo antagonista de EPAC no nucleótido cíclico, capaz de bloquear específicamente la activación intracelular de Rap1 mediada por EPAC y la fosforilación de Akt, así como la secreción de insulina mediada por EPAC en células β pancreáticas. Por otro lado, este compuesto no logra suprimir la fosforilación de Akt inducida por el factor de crecimiento epidérmico (EGF) en células AsPC1. En células de cáncer de páncreas, este antagonista inhibe la migración e invasión celular al disminuir la adhesión celular inducida por 007-AM de manera dosis-dependiente. Este químico reduce significativamente el recuento de bacterias intracelulares y totales en células endoteliales de la vena umbilical humana. Antagoniza eficazmente la diferenciación de células de Schwann (SC) inducida por CPT-cAMP, así como la formación de mielina. En cultivos de SC-neuronas, este compuesto reduce drásticamente el número de SCs O1 positivas y MBP positivas sin comprometer la salud de las neuronas o las SCs mismas. | ||||
| In vivo | ESI-09 (10 mg/kg/día, i.p.), mediante la inhibición farmacológica de EPAC1, protege a los ratones WT C57BL/6 de la rickettsiosis SFG mortal. |
Protocolo (de referencia)
| Estudio en animales:[2] |
|
|---|
Referencias
|
Validación de productos por parte del cliente
-
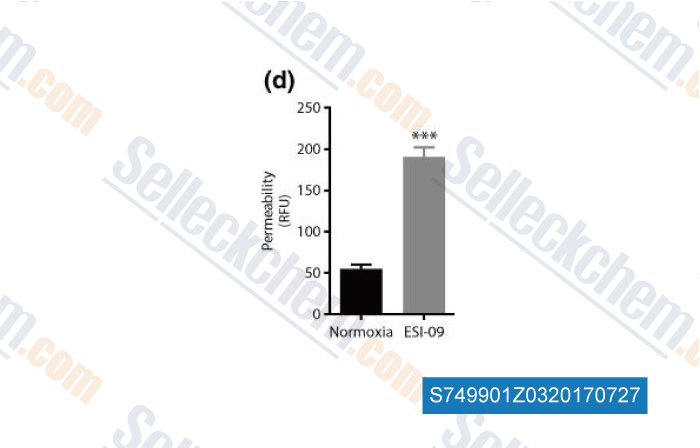
, , Brain Behav Immun, 2016, 58:118-129.
-
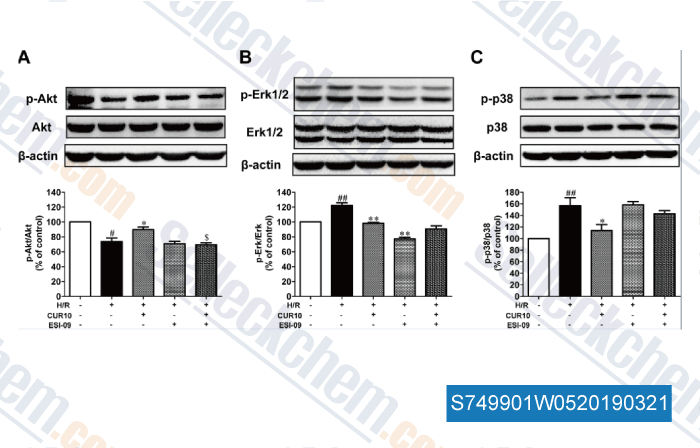
Datos de [ , , Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 109:1268-1275 ]
-
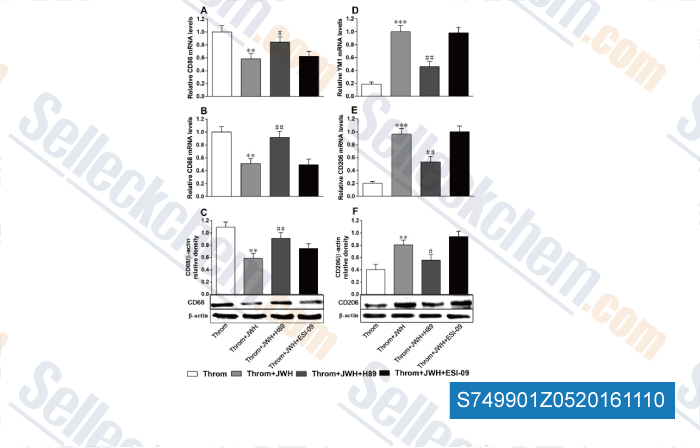
Datos de [ , , Acta Diabetol, 2017, 54(6):581-591 ]
-
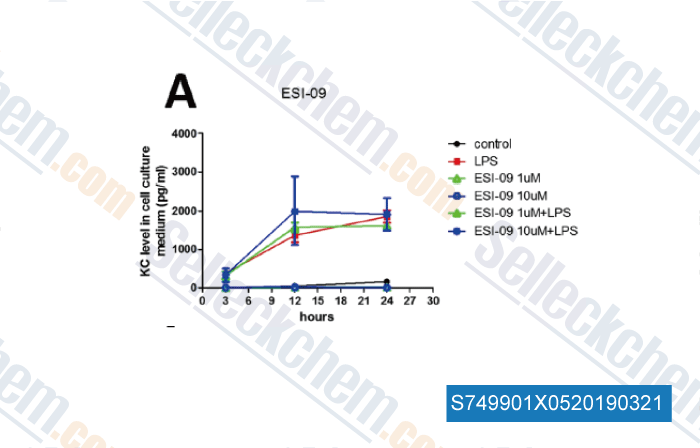
Datos de [ , , Inflammation, 2018, 41(3):1093-1103 ]
Sellecks ESI-09 Ha sido citado por 14 Publicaciones
| Ginsenoside Ro prevents endothelial injury via promoting Epac1/AMPK- mediated mitochondria protection in early diabetic retinopathy [ Pharmacol Res, 2025, 211:107562] | PubMed: 39732351 |
| Inhibition of exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP as a strategy for broad-spectrum antiviral development [ J Biol Chem, 2023, 299(6):104749] | PubMed: 37100284 |
| PNX14 but not PNX20 as a novel regulator of preadipocyte differentiation via activating Epac-ERK signaling pathway in Gallus gallus [ Gen Comp Endocrinol, 2023, 335:114232] | PubMed: 36774983 |
| Vitexin Mitigates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Regulating Mitochondrial Dysfunction via Epac1-Rap1 Signaling [ Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021:9921982] | PubMed: 34257823 |
| Terbutaline attenuates LPS-induced injury of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells by cAMP/Epac signaling [ Drug Dev Res, 2021, 10.1002/ddr.21901] | PubMed: 34846077 |
| Knockdown of GPSM1 Inhibits the Proliferation and Promotes the Apoptosis of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells by Suppressing the ADCY6-RAPGEF3-JNK Signaling Pathway [ Pathol Oncol Res, 2021, 27:643376] | PubMed: 34257610 |
| Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac) 1 plays an essential role in stress-induced exercise capacity by regulating PGC-1α and fatty acid metabolism in skeletal muscle. [ Pflugers Arch, 2020, 472(2):195-216] | PubMed: 31955265 |
| Curcumin pretreatment protects against hypoxia/reoxgenation injury via improvement of mitochondrial function, destabilization of HIF-1α and activation of Epac1-Akt pathway in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [Wang X, et al. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 109:1268-1275] | PubMed: 30551377 |
| Protective Effect of Quercetin in LPS-Induced Murine Acute Lung Injury Mediated by cAMP-Epac Pathway [Wang XF, et al. Inflammation, 2018, 41(3):1093-1103] | PubMed: 29569077 |
| Activation of Epac alleviates inflammation and vascular leakage in LPS-induced acute murine lung injury [Wang X, et al. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 96:1127-1136] | PubMed: 29174852 |
POLÍTICA DE DEVOLUCIÓN
La Política de Devolución Incondicional de Selleck Chemical garantiza una experiencia de compra en línea fluida para nuestros clientes. Si no está satisfecho con su compra de alguna manera, puede devolver cualquier artículo(s) dentro de los 7 días posteriores a su recepción. En caso de problemas de calidad del producto, ya sean problemas relacionados con el protocolo o con el producto, puede devolver cualquier artículo(s) dentro de los 365 días a partir de la fecha de compra original. Siga las instrucciones a continuación al devolver productos.
ENVÍO Y ALMACENAMIENTO
Los productos Selleck se transportan a temperatura ambiente. Si recibe el producto a temperatura ambiente, tenga la seguridad de que el Departamento de Inspección de Calidad de Selleck ha realizado experimentos para verificar que la colocación a temperatura normal durante un mes no afectará la actividad biológica de los productos en polvo. Después de la recogida, guarde el producto de acuerdo con los requisitos descritos en la hoja de datos. La mayoría de los productos Selleck son estables en las condiciones recomendadas.
NO PARA USO HUMANO, DIAGNÓSTICO VETERINARIO O TERAPÉUTICO.
