Datos técnicos
| Fórmula | C29H43NO4S |
||||||
| Peso molecular | 501.72 | Número CAS | 166518-60-1 | ||||
| Solubilidad (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 100 mg/mL (199.31 mM) | ||||
| Ethanol | 15 mg/mL (29.89 mM) | ||||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Agregue los solventes al producto individualmente y en orden.) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml significa ligeramente soluble o insoluble. * Tenga en cuenta que Selleck prueba la solubilidad de todos los compuestos internamente, y la solubilidad real puede diferir ligeramente de los valores publicados. Esto es normal y se debe a ligeras variaciones entre lotes. * Envío a temperatura ambiente (Las pruebas de estabilidad demuestran que este producto se puede enviar sin medidas de refrigeración.) |
|||||||
Preparación de soluciones madre
Actividad biológica
| Descripción | Avasimibe inhibe la ACAT con una IC50 de 3,3 μM, y también inhibe las isoenzimas humanas P450 CYP2C9, CYP1A2 y CYP2C19 con una IC50 de 2,9 μM, 13,9 μM y 26,5 μM, respectivamente. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objetivos |
|
||||||||
| In vitro | Avasimibe, a una concentración de 1 μg/mL, provoca una reducción del colesterol total (TC) y del colesterol esterificado (EC) al inhibir la unión del LDL y disminuir el número de receptores depuradores durante la formación de células espumosas en macrófagos derivados de monocitos humanos (HMMs). Este compuesto, a una concentración de 2 μg/mL, mejora el eflujo de colesterol de las células espumosas HMM establecidas preincubadas con 10 μg/ml de LDL. Inhibe la acumulación de Lipoproteína(a) en los medios de cultivo de hepatocitos primarios de mono de manera dosis-dependiente con una inhibición del 11,9% al 31,3%, el cambio se asocia principalmente con una disminución de ApoA. Esta sustancia química, incubada a concentraciones de 10 nM, 1 μM y 10 μM durante 24 horas en células HepG2, reduce la secreción de ApoB en los medios en un 25%, 27% y 43%, respectivamente. Disminuye la secreción de ApoB mediante una degradación intracelular mejorada de ApoB en lugar de una síntesis disminuida de ApoB. El compuesto inhibe la ACTC con una IC50 de 3,3 μM en macrófagos IC-21, considerando la concentración total del inhibidor en la muestra del ensayo. Inhibe las isoenzimas humanas P450 CYP2C9, CYP1A2 y CYP2C19 con una IC50 de 2,9 μM, 13,9 μM y 26,5 μM, respectivamente. Este inhibidor inhibe la expresión de ACAT-1 y la síntesis de ésteres de colesterol en líneas celulares de glioma. Inhibe el crecimiento de las células de glioma induciendo la detención del ciclo celular y la apoptosis debido a la activación de la caspasa-8 y la caspasa-3. |
||||||||
| In vivo | Avasimibe reduce significativamente los niveles de Lipoproteína(a) y de colesterol total en nueve monos macho sanos con una dieta de chow normal tratados oralmente con CI-1011 a 30 mg/kg por día durante 3 semanas; los niveles de Lipoproteína(a) y de colesterol total se reducen a 68 y 73% de los niveles de control, respectivamente. Este compuesto disminuye el colesterol total principalmente debido a la reducción de lipoproteínas de baja densidad (LDL). Disminuye la carga de placas amiloides en la corteza y el hipocampo y reduce los niveles de Abeta40 y Abeta42 insolubles y de fragmentos C-terminales de la proteína precursora amiloide (APP) en extractos cerebrales en ratones transgénicos APP humanos jóvenes. Este producto químico reduce las placas amiloides difusas mediante la supresión de la astrogliosis y la activación microglial mejorada en ratones transgénicos APP humanos envejecidos. |
Protocolo (de referencia)
| Ensayo de quinasa: |
|
|---|---|
| Ensayo celular: |
|
| Estudio en animales: |
|
Referencias
|
Validación de productos por parte del cliente
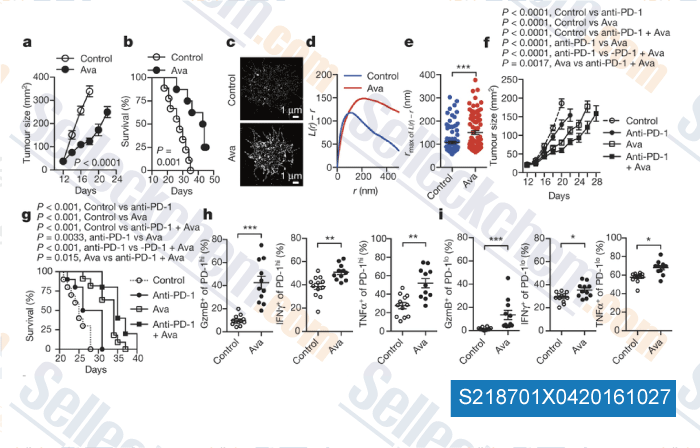
-
, , Nature, 2016, 531(7596):651-5.
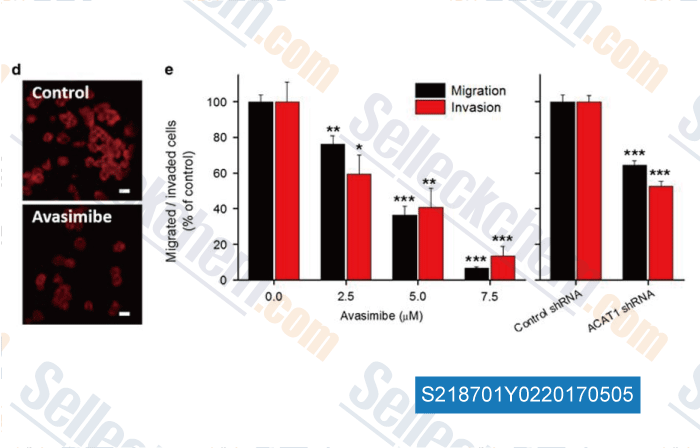
-
Datos de [ , , Oncogene, 2016, 35(50):6378-6388 ]
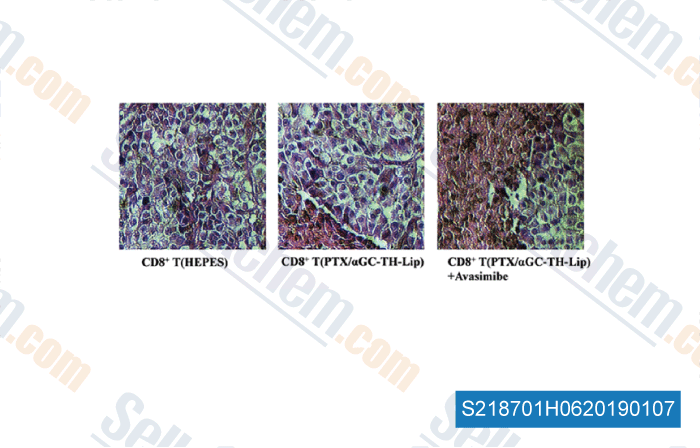
-
Datos de [ , , Nanomedicine, 2018, 14(8):2541-2550 ]
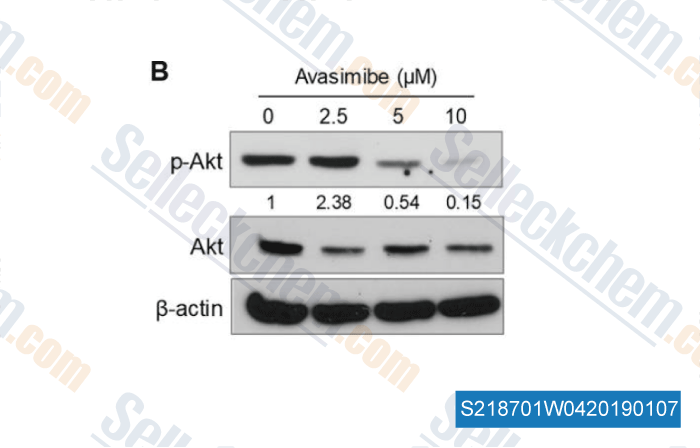
-
Datos de [ , , PLoS One, 2018, 13(2):e0193318 ]
Sellecks Avasimibe Ha sido citado por 25 Publicaciones
| Functional characterization of genetic variants affecting the intracellular domains of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) [ J Lipid Res, 2025, 66(8):100854] | PubMed: 40617357 |
| Antioxidant interventions reduced cytokine-induced pyroptosis of peripheral MAIT cells in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis [ Hepatol Commun, 2025, 9(6)e0714] | PubMed: 40377492 |
| Specific activation of the integrated stress response uncovers regulation of central carbon metabolism and lipid droplet biogenesis [ Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1):8301] | PubMed: 39333061 |
| Stimulation of neutral lipid synthesis via viral growth factor signaling and ATP citrate lyase during vaccinia virus infection [ J Virol, 2024, 98(11):e0110324] | PubMed: 39475274 |
| An ACAT inhibitor suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and boosts antiviral T cell activity [ PLoS Pathog, 2023, 19(5):e1011323] | PubMed: 37134108 |
| Metabolic interventions improve HBV envelope-specific T-cell responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B [ Hepatol Int, 2023, 10.1007/s12072-023-10490-4] | PubMed: 36976426 |
| Cholesterol mediated ferroptosis suppression reveals essential roles of Coenzyme Q and squalene [ Commun Biol, 2023, 6(1):1108] | PubMed: 37914914 |
| Avasimibe Alleviates Disruption of the Airway Epithelial Barrier by Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway [ Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13:795934] | PubMed: 35222024 |
| Targeting cholesterol esterification as a novel immune checkpoint in viral infections and cancer [ UCL-, 2022, ] | PubMed: None |
| Targeting human Acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase as a dual viral and T cell metabolic checkpoint [ Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1):2814] | PubMed: 33990561 |
POLÍTICA DE DEVOLUCIÓN
La Política de Devolución Incondicional de Selleck Chemical garantiza una experiencia de compra en línea fluida para nuestros clientes. Si no está satisfecho con su compra de alguna manera, puede devolver cualquier artículo(s) dentro de los 7 días posteriores a su recepción. En caso de problemas de calidad del producto, ya sean problemas relacionados con el protocolo o con el producto, puede devolver cualquier artículo(s) dentro de los 365 días a partir de la fecha de compra original. Siga las instrucciones a continuación al devolver productos.
ENVÍO Y ALMACENAMIENTO
Los productos Selleck se transportan a temperatura ambiente. Si recibe el producto a temperatura ambiente, tenga la seguridad de que el Departamento de Inspección de Calidad de Selleck ha realizado experimentos para verificar que la colocación a temperatura normal durante un mes no afectará la actividad biológica de los productos en polvo. Después de la recogida, guarde el producto de acuerdo con los requisitos descritos en la hoja de datos. La mayoría de los productos Selleck son estables en las condiciones recomendadas.
NO PARA USO HUMANO, DIAGNÓSTICO VETERINARIO O TERAPÉUTICO.
